Page 10 - reflections_dyslipidaemia_newsletter9_Final
P. 10
REFLECTIONS
Dyslipidaemia
Dyslipidaemia Global Newsletter #9 2025
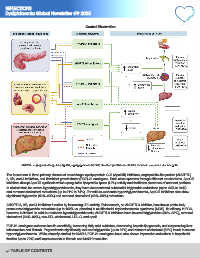
Central illustration Dyslipidaemia
ANGPTL, angiopoietin-like protein; ApoCIII, apolipoprotein C-III; FGF, fibroblast growth factor; MASH, metabolic-associated steatohepatitis.
The focus here is three primary classes of novel drugs: apolipoprotein C-III (ApoCIII) inhibitors, angiopoietin-like protein (ANGPTL)
3, 3/8, and 4 inhibitors, and fibroblast growth factor (FGF)-21 analogues. Each class operates through different mechanisms. ApoCIII
inhibitors disrupt ApoCIII synthesis which upregulates lipoprotein lipase (LPL) activity and facilitates clearance of remnant particles.
In clinical trials for severe hypertriglyceridaemia, they have demonstrated substantial triglyceride reductions (up to 44% to 94%)
and remnant cholesterol reductions (up to 31% to 74%). For mild-to-moderate hypertriglyceridaemia, ApoCIII inhibitors also show
significant triglyceride (59%–63%) and remnant cholesterol (48%–59%) reductions.
ANGPTL3, 3/8, and 4 inhibitors function by increasing LPL activity. Evinacumab, an ANGPTL3 inhibitor, has shown particularly
pronounced triglyceride reductions (up to 162% vs. placebo) in multifactorial chylomicronemia syndrome (MCS). Its efficacy in FCS,
however, is limited. In mild-to-moderate hypertriglyceridaemia, ANGPTL3 inhibitors have lowered triglycerides (56%–63%), remnant
cholesterol (64%–82%), non-HDL cholesterol, LDL-C, and apoB.
FGF-21 analogues enhance insulin sensitivity, increasing fatty acid oxidation, decreasing hepatic lipogenesis, and suppressing liver
inflammation and fibrosis. Pegozafermin significantly reduced triglyceride (up to 67%) and remnant cholesterol (52%) levels in severe
hypertriglyceridaemia. While primarily studied for MASH, FGF-21 analogues have also shown impressive reductions in hepatic fat
fraction (up to 72%) and improvements in fibrosis and MASH resolution.
TABLE OF CONTENTS